Navigation
This guide describes the navigation events, and shows how to load URLs and files, filter navigation requests, work with navigation history, etc.
Loading URL
To navigate to a resource identified by a URL you can use one of the following methods:
Navigation.loadUrl(String url)Navigation.loadUrl(LoadUrlParams params)
The following example shows how to navigate to https://www.google.com using the Navigation.loadUrl(String) method:
var navigation = browser.navigation();
navigation.loadUrl("https://html5test.teamdev.com");
val navigation = browser.navigation
navigation.loadUrl("https://html5test.teamdev.com")
The code above requests navigation to the given resource and exits immediately. It does not wait until the resource is loaded completely.
If you need to block the current thread execution until the resource is loaded completely, use
the Navigation.loadUrlAndWait() method:
// Wait with the default timeout of 45 seconds.
navigation.loadUrlAndWait("https://html5test.teamdev.com");
// Wait with the custom timeout.
navigation.loadUrlAndWait("https://html5test.teamdev.com", Duration.ofSeconds(30));
// Wait with the default timeout of 45 seconds.
navigation.loadUrlAndWait("https://html5test.teamdev.com")
// Wait with the custom timeout.
navigation.loadUrlAndWait("https://html5test.teamdev.com", Duration.ofSeconds(30))
This method blocks the current thread execution until the main frame of the resource is loaded completely or until the
given timeout is reached. If the resource has not been loaded within a timeout, the TimeoutException exception
will be thrown.
You can get the current value of the default timeout using the Navigation.defaultTimeout() method:
Duration timeout = Navigation.defaultTimeout();
val timeout: Duration = Navigation.defaultTimeout()
If navigation fails, the NavigationException exception will be thrown.
Loading URL with POST
To load a web page and send POST data, use the Navigation.loadUrl(LoadUrlParams) method. The following code
demonstrates how to send the plain text POST data to a URL:
var data = TextData.of("post data");
var params = LoadUrlParams.newBuilder(url)
.uploadData(data)
.addExtraHeader(HttpHeader.of("header name", "header value"))
.build();
navigation.loadUrl(params);
val params = LoadUrlParams(
url = url,
data = TextData("post data"),
extraHeaders = listOf(
HttpHeader("header name", "header value")
)
)
navigation.loadUrl(params)
Besides the plain text data, you can send FormData, MultipartFormData or arbitrary ByteData:
import com.teamdev.jxbrowser.net.File;
...
var avatarFile = File.newBuilder()
.bytesValue(avatarBytes)
.contentType("image/png")
.build();
var data = MultipartFormData.newBuilder()
.addPair(Pair.of("user", "john"))
.addPair(Pair.of("avatar", avatarFile))
.build();
var data = FormData.newBuilder()
.addPair(Pair.of("street", "Forthlin Rd"))
.addPair(Pair.of("house", "20"))
.build();
// From the string.
var message = ByteData.of("from string");
// From the byte array.
var avatar = ByteData.of(imageBytes);
// With the specific content type.
var pdf = ByteData.of(
pdfBytes,
ContentType.newBuilder("application/pdf").build()
);
JxBrowser will automatically inject the Content-Type and Content-Length headers.
In the multipart case, it will also include the form boundary plus each part’s
Content-Disposition and Content-Type.
The default content types are:
text/plainforTextDataapplication/octet-streamforByteDataapplication/x-www-form-urlencodedforFormDatamultipart/form-dataforMultipartFormData
If you need to override the default Content-Type or Content-Length headers, add your own values
as extra headers in LoadUrlParams.
Loading local content
You can load local content in several ways, and each way has specific capabilities and limitations. The following sections explains how to choose the approach that best fits your use case.
Loading files from disk
The most direct way to load an HTML file is to use a file:// URL:
navigation.loadUrl(new File("index.html").getAbsolutePath());
val indexPage = File("index.html")
navigation.loadUrl(indexPage.absolutePath)
Be aware, that loading pages using file:// comes with important limitations. When you load content
this way, Chromium applies stricter security rules than it does for regular HTTP or HTTPS pages.
Pages loaded using the file:// scheme are subject to the following limitations:
- A page cannot reference local resources outside its own directory.
- A page cannot dynamically load resources via JavaScript.
- Chromium blocks these pages from making HTTP requests to remote servers.
- JavaScript APIs that require a secure context may not function under the
file://scheme.
Use this approach with caution, as the restrictions in Chromium may change between releases without prior notice.
Loading HTML
You can load arbitrary HTML strings into JxBrowser by converting them to a data URI:
The idea of this approach is to convert the required HTML to a base64 string,
generate the Data URI with the converted string, and load this URL
as shown below:
var html = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>";
var base64Html = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(html.getBytes(UTF_8));
var dataUrl = "data:text/html;charset=utf-8;base64," + base64Html;
browser.navigation().loadUrl(dataUrl);
val html = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>"
val base64Html = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(html.toByteArray(UTF_8))
val dataUrl = "data:text/html;charset=utf-8;base64,$base64Html"
browser.navigation.loadUrl(dataUrl)
You can also use the Navigation.loadHtml(String html) method, which automatically generates the data URI from the
given HTML:
var html = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>";
browser.navigation().loadHtml(html);
val html = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>"
browser.navigation.loadHtml(html)
Pages loaded through data URIs are subject to the following limitations:
- The URL string must not exceed 2 MB due to the Chromium limit. Any attempt to load a longer URL is ignored by Chromium.
- Such pages cannot send requests to HTTPS servers or reference HTTPS resources, because Chromium treats data URLs as an insecure context.
- Such pages are not permitted to use local storage.
- Anchor navigation is not supported.
Loading by intercepting requests
Another way to load local content is to intercept network requests and substitute the response with the content you want to deliver.
This approach requires manual implementation, but it provides fine-grained control over the process:
- You can load any type of data: HTML, images, JSON, and more.
- You can set arbitrary HTTP response headers, including
Content-TypeandCookie. - You can load large amounts of data asynchronously.
In this approach, you register an InterceptUrlRequestCallback that intercepts requests made under https:// or
another chosen scheme and lets you construct the response at runtime:
// This callback intercepts requests with the `?hello` parameter and returns
// `<html><body>Hello</body></html>` as the response.
InterceptUrlRequestCallback interceptCallback = params -> {
if (params.urlRequest().url().endsWith("?hello")) {
var bytes = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>".getBytes();
var job = params.newUrlRequestJob(
UrlRequestJob.Options
.newBuilder(HttpStatus.OK)
.addHttpHeader(HttpHeader.of("Content-Type", "text/html"))
.build()
);
job.write(bytes);
job.complete();
return InterceptUrlRequestCallback.Response.intercept(job);
}
return InterceptUrlRequestCallback.Response.proceed();
};
var options = EngineOptions.newBuilder(renderingMode)
.addScheme(HTTP, interceptCallback)
.build();
var engine = Engine.newInstance(options);
var browser = engine.newBrowser();
browser.navigation().loadUrl("http://load.html/?hello");
// This callback intercepts requests with the `?hello` parameter and returns
// `<html><body>Hello</body></html>` as the response.
val interceptCallback = InterceptUrlRequestCallback { params ->
if (params.urlRequest().url().endsWith("?hello")) {
val bytes = "<html><body>Hello</body></html>".toByteArray()
val options = UrlRequestJobOptions(
status = HttpStatus.OK,
headers = listOf(HttpHeader("Content-Type", "text/html"))
)
val job = params.newUrlRequestJob(options).apply {
write(bytes)
complete()
}
InterceptUrlRequestCallback.Response.intercept(job)
} else {
InterceptUrlRequestCallback.Response.proceed()
}
}
val engine = Engine(renderingMode) {
schemes.add(HTTP, interceptCallback)
}
val browser = engine.newBrowser()
browser.navigation.loadUrl("http://load.html/?hello")
In addition to standard HTTP and HTTPS schemes, you can intercept requests to custom protocols:
// This will intercept all requests to my-app://
var options = EngineOptions.newBuilder(renderingMode)
.addScheme(Scheme.of("my-app"), interceptCallback)
.build();
// This will intercept all requests to my-app://
val engine = Engine(renderingMode) {
schemes.add(Scheme("my-app"), interceptCallback)
}
Chromium treats custom protocols as a secure context, allowing full use of JavaScript APIs and network requests just as on a standard HTTPS page.
For more details, see the tutorial on loading local resources with request interceptors.
Reloading
There are several options to reload the currently loaded web page:
Reload using HTTP cache:
navigation.reload();
navigation.reload()
Reload ignoring HTTP cache:
navigation.reloadIgnoringCache();
navigation.reloadIgnoringCache()
Reload using HTTP cache and check for repost:
navigation.reloadAndCheckForRepost();
navigation.reloadAndCheckForRepost()
Reload ignoring HTTP cache and check for repost:
navigation.reloadIgnoringCacheAndCheckForRepost();
navigation.reloadIgnoringCacheAndCheckForRepost()
Stopping
Use the Navigation.stop() method to cancel any pending navigation or download operation, and stop any dynamic page elements, such as background sounds and animations. For example:
navigation.stop();
navigation.stop()
Back & forward
JxBrowser allows working with the navigation back-forward history list.
When you create a Browser instance it navigates to the about:blank web page by default, so there is always one entry in the navigation back-forward list.
To load the previous location in the back-forward list use the following approach:
if (navigation.canGoBack()) {
navigation.goBack();
}
if (navigation.canGoBack) {
navigation.goBack()
}
To load the next location in the back-forward list use:
if (navigation.canGoForward()) {
navigation.goForward();
}
if (navigation.canGoForward) {
navigation.goForward()
}
To navigate to the entry at a specific index in the back-forward list use:
if (index >= 0 && index < navigation.entryCount()) {
navigation.goToIndex(index);
}
if (index >= 0 && index < navigation.entryCount()) {
navigation.goToIndex(index)
}
You can go through the back-forward list and get the details about every navigation entry:
for (int index = 0; index < navigation.entryCount(); index++) {
var navigationEntry = navigation.entryAtIndex(index);
System.out.println("URL: " + navigationEntry.url());
System.out.println("Title: " + navigationEntry.title());
}
for (index in 0 until navigation.entryCount()) {
val navigationEntry = navigation.entryAtIndex(index)
println("URL: ${navigationEntry.url()}")
println("Title: ${navigationEntry.title()}")
}
You can modify the back-forward list by removing the entries:
// Returns the number of entries in the back/forward list.
var entryCount = navigation.entryCount();
// Remove navigation entries at index.
for (int i = entryCount - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
var success = navigation.removeEntryAtIndex(i);
System.out.println("Was the navigation entry at the index " + i +
" successfully removed? " + success);
}
// Returns the number of entries in the back/forward list.
val entryCount = navigation.entryCount()
// Remove navigation entries at index.
for (i in entryCount - 2 downTo 0) {
val success = navigation.removeEntryAtIndex(i)
println("Was the navigation entry at the index $i successfully removed? $success")
}
Filtering URLs
You can decide whether navigation request to a specific URL should be ignored or not.
The following code demonstrates how to ignore navigation requests to all URLs that start with https://www.google:
navigation.set(StartNavigationCallback.class, params -> {
// Ignore navigation requests to the URLs that start
// with "https://www.google".
if (params.url().startsWith("https://www.google")) {
return StartNavigationCallback.Response.ignore();
}
return StartNavigationCallback.Response.start();
});
navigation.register(StartNavigationCallback { params ->
// Ignore navigation requests to the URLs that start
// with "https://www.google".
if (params.url().startsWith("https://www.google")) {
StartNavigationCallback.Response.ignore()
} else {
StartNavigationCallback.Response.start()
}
})
Customizing error pages
When a Chromium encounters an HTTP or a network error, it shows the default error page. In JxBrowser, you can replace that page with your own.
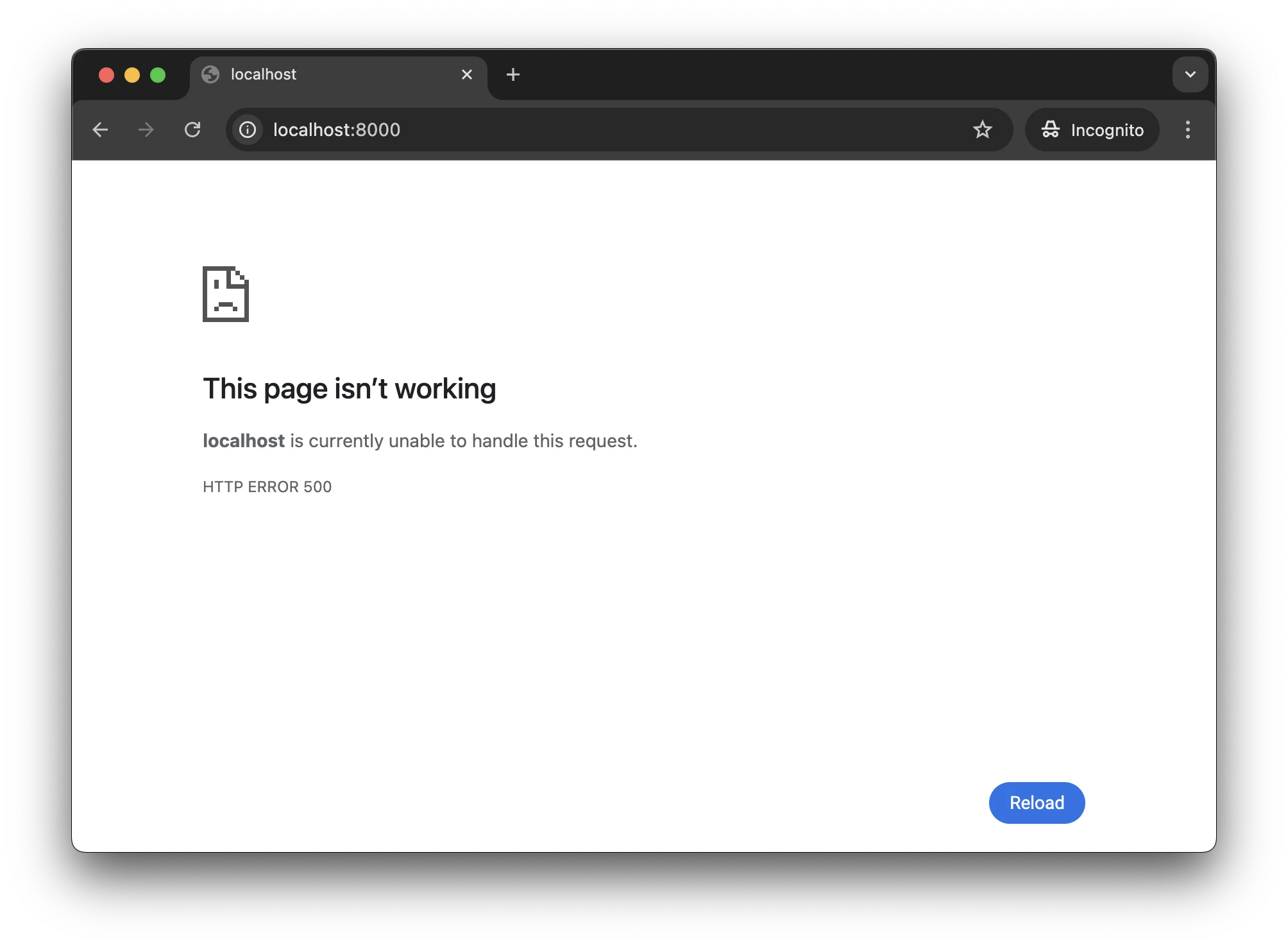
To replace an error page that occurs when Chromium receives an HTTP error with an empty response from the server,
use ShowHttpErrorPageCallback:
navigation.set(ShowHttpErrorPageCallback.class, params -> {
var url = params.url();
var httpStatus = params.httpStatus();
if (httpStatus == NOT_FOUND) {
// Show a custom HTML page.
return ShowHttpErrorPageCallback.Response.show(
"<p>Oops! Not found!</p>");
} else {
// Show the default Chromium error page.
return ShowHttpErrorPageCallback.Response.showDefault();
}
});
navigation.register(ShowHttpErrorPageCallback { params ->
val url = params.url()
val httpStatus = params.httpStatus()
if (httpStatus === NOT_FOUND) {
// Show a custom HTML page.
ShowHttpErrorPageCallback.Response.show(
"<p>Oops! Not found!</p>"
)
} else {
// Show the default Chromium error page.
ShowHttpErrorPageCallback.Response.showDefault()
}
})
To replace an error page that occurs when Chromium encounters a network error, use ShowNetErrorPageCallback:
navigation.set(ShowNetErrorPageCallback.class, params -> {
var url = params.url();
var error = params.error();
if (error == CERT_DATE_INVALID) {
// Show a custom HTML page.
return ShowNetErrorPageCallback.Response.show(
"<p>Invalid certificate!</p>");
} else {
// Show the default Chromium error page.
return ShowNetErrorPageCallback.Response.showDefault();
}
});
navigation.register(ShowNetErrorPageCallback { params ->
val url = params.url()
val error = params.error()
if (error == CERT_DATE_INVALID) {
// Show a custom HTML page.
ShowNetErrorPageCallback.Response.show(
"<p>Invalid certificate!</p>"
)
} else {
// Show the default Chromium error page.
ShowNetErrorPageCallback.Response.showDefault()
}
})
Canceling and redirecting URL requests
Use the BeforeUrlRequestCallback callback to control whether a URL request should be canceled, redirected, or handled
normally. This callback is useful for selectively blocking the loading of resources such as HTML, images, CSS, etc.
By default, all requests are processed normally. To modify this behavior, register your own callback implementation and decide how to proceed with each individual request.
The following example demonstrates how to:
- block the loading of images;
- redirect requests to .htm files to .html files;
- handle the remaining requests as usual.
var network = engine.network();
network.set(BeforeUrlRequestCallback.class, params -> {
var urlRequest = params.urlRequest();
if (urlRequest.resourceType() == IMAGE) {
return BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.cancel();
}
if (urlRequest.url().endsWith(".htm")) {
var newUrl = urlRequest.url() + "l";
return BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.redirect(newUrl);
}
return BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.proceed();
});
val network = engine.network
network.register(BeforeUrlRequestCallback { params ->
val urlRequest = params.urlRequest()
if (urlRequest.resourceType() === IMAGE) {
BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.cancel()
} else if (urlRequest.url().endsWith(".htm")) {
val newUrl = urlRequest.url() + "l";
BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.redirect(newUrl)
} else {
BeforeUrlRequestCallback.Response.proceed()
}
})
Navigation events
Loading a web page is a complex process during which different navigation events are fired. The following diagram shows the order in which the navigation events might be fired when loading a web page:
Load started
To get notifications when content loading has started please use the LoadStarted event. For example:
navigation.on(LoadStarted.class, event -> {});
navigation.subscribe<LoadStarted> { event -> }
This event corresponds to the moment when the spinner of the tab starts spinning.
Load finished
To get notifications when content loading has finished please use the LoadFinished event. For example:
navigation.on(LoadFinished.class, event -> {});
navigation.subscribe<LoadStarted> { event -> }
This event corresponds to the moment when the spinner of the tab stops spinning.
Navigation started
To get notifications when navigation has started please use the NavigationStarted event. For example:
navigation.on(NavigationStarted.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
// Indicates whether the navigation will be performed
// in the scope of the same document.
var isSameDocument = event.isSameDocument();
});
navigation.subscribe<NavigationStarted> { event ->
val url = event.url()
// Indicates whether the navigation will be performed
// in the scope of the same document.
val isSameDocument = event.isSameDocument
}
Navigation stopped
To get notifications when navigation has stopped please use the NavigationStopped event. For example:
navigation.on(NavigationStopped.class, event -> {});
navigation.subscribe<NavigationStopped> { event -> }
This event is fired when navigation is stopped via the Navigation.stop() method.
Navigation redirected
To get notifications when navigation has been redirected to a new URL please use the NavigationRedirected event. For example:
navigation.on(NavigationRedirected.class, event -> {
// The navigation redirect URL.
var url = event.destinationUrl();
});
navigation.subscribe<NavigationRedirected> { event ->
// The navigation redirect URL.
val url = event.destinationUrl()
}
Navigation finished
To get notifications when navigation has finished please use the NavigationFinished event. For example:
navigation.on(NavigationFinished.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
var frame = event.frame();
var hasCommitted = event.hasCommitted();
var isSameDocument = event.isSameDocument();
var isErrorPage = event.isErrorPage();
if (isErrorPage) {
var error = event.error();
}
});
navigation.subscribe<NavigationFinished> { event ->
val url = event.url()
val frame = event.frame()
val hasCommitted = event.hasCommitted()
val isSameDocument = event.isSameDocument
val isErrorPage = event.isErrorPage
if (isErrorPage) {
val error = event.error()
}
}
This event is fired when navigation is committed, aborted, or replaced by a new one. To know if the navigation has committed, use NavigationFinished.hasCommitted(); use NavigationFinished.isErrorPage() to know if the navigation resulted in an error page.
If the event is called because the navigation committed, the document load will still be ongoing.
The event is fired by same-document (in the scope of the same document) navigations, such as fragment navigations or window.history.pushState()/window.history.replaceState(), which will not result in a document change. Please use NavigationFinished.isSameDocument() to check if it is a same-document navigation.
Frame load finished
To get notifications when content loading in the Frame has finished please use the FrameLoadFinished event. For example:
navigation.on(FrameLoadFinished.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
var frame = event.frame();
});
navigation.subscribe<FrameLoadFinished> { event ->
val url = event.url()
val frame = event.frame()
}
This event corresponds to the moment when the content in the Frame has been loaded completely.
Frame load failed
To get notifications when content loading in the Frame has failed for some reason, use the FrameLoadFailed event. For example:
navigation.on(FrameLoadFailed.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
var error = event.error();
});
navigation.subscribe<FrameLoadFailed> { event ->
val url = event.url()
val error = event.error()
}
Frame document load finished
To get notifications when the document loading in the Frame has finished please use the FrameDocumentLoadFinished event. For example:
navigation.on(FrameDocumentLoadFinished.class, event -> {
var frame = event.frame();
});
navigation.subscribe<FrameDocumentLoadFinished> { event ->
val frame = event.frame()
}
At this point, deferred scripts were executed, and the content scripts marked “document_end” get injected into the frame.
Loading PDF files
When loading PDF files into the browser, use the PdfDocumentLoaded event to detect
when the document is loaded:
browser.on(PdfDocumentLoaded.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
var frame = event.frame();
// This event is a good place to start PDF printing.
frame.print();
});
browser.subscribe<PdfDocumentLoaded> { event ->
val url = event.url()
val frame = event.frame()
// This event is a good place to start PDF printing.
frame.print()
}
The document may not be loaded because of an unexpected error: network failure, incorrect password,
corrupt PDF file, etc. In that case, JxBrowser will emit the PdfDocumentLoadFailed event:
browser.on(PdfDocumentLoadFailed.class, event -> {
var url = event.url();
var frame = event.frame();
});
browser.subscribe<PdfDocumentLoadFailed> { event ->
val url = event.url()
val frame = event.frame()
}
Note that the Navigation.loadUrlAndWait() method and the FrameLoadFinished event should not be used to wait for a PDF document
to load.
